The 2020s will be a crucial period for all participants in the power industry as the transition toward carbon-neutral fuels is expected to increase, while fossil fuels take a downturn in most developed markets. This is according to Frost & Sullivan’s recent analysis, “Growth Opportunities from Decarbonization in the Global Power Market, 2019-2030”. Falling costs, emphasis on climate change mitigation and environment-friendly energy policies adopted by several countries in the six major geographies: North America, Latin America, Europe, the Middle East, China, and India, are prominent reasons why decentralization, decarbonization, and digitalization will become the three key pillars of the global energy transformation. An estimated USD3.4 trillion will be invested in renewables during the next decade and by 2030, 54% of installed capacity will be renewable.
The power sector will witness strong growth in decentralization during the next decade, with annual global investment increasing from USD53 billion in 2019 to USD93 billion in 2030. Pressure will continue to build for further decarbonization within the power sector as the rate of adoption of digital technologies increases in both existing and future plants to boost operational performance. The need for flexibility is the most significant trend observed across all markets. System operators are coming under increasing pressure to manage the system with uncertain renewable output, declining base load, transmission bottle-necks, and demand-side variability. As a result, technologies and solutions such as decentralized power generation, battery energy storage systems, demand-side response, and virtual power plants are witnessing unprecedented adoption rates amongst utilities, solution providers, and end-consumers.
 The UN Policy Brief #24 on accelerating SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) achievement through energy sector transformation supports the same conclusion: decentralized power generation is paramount for universal energy access. Business as usual governance of the energy sector will not be able to achieve universal energy access, in particular with regard to renewable energy. Since large scale on-grid energy production has proven less cost effective for providing access outside densely populated areas, decentralized power generation, mini-grid and off-grid energy systems are essential to achieving universal access by 2030 in the most cost- and time-efficient manner. In addition, timely access to energy would mitigate the opportunity costs associated with better livelihoods and economic prosperity, which are fundamental aspects to achieving other United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs).
The UN Policy Brief #24 on accelerating SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) achievement through energy sector transformation supports the same conclusion: decentralized power generation is paramount for universal energy access. Business as usual governance of the energy sector will not be able to achieve universal energy access, in particular with regard to renewable energy. Since large scale on-grid energy production has proven less cost effective for providing access outside densely populated areas, decentralized power generation, mini-grid and off-grid energy systems are essential to achieving universal access by 2030 in the most cost- and time-efficient manner. In addition, timely access to energy would mitigate the opportunity costs associated with better livelihoods and economic prosperity, which are fundamental aspects to achieving other United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs).
The deployment of decentralized energy is fueling a disruptive transformation of the energy sector. The rapid growth of decentralized energy technologies changes the structure of the energy sector towards a multi-actor set-up in which large utilities interact with self-producing consumers and mini-utilities. Decentralized power generation will drive energy solutions that are more in line with people’s and companies’ needs, in particular those who prioritize energy services with major development co-benefits. The decentralized power generation is able to provide a wider mix of energy commodities locally, and with higher efficiency saving significant transmission losses and fuel transportation costs. The focus of energy access is therefore not just wires and poles, but quality supply that supports local economic activities. This, in turn, will drive a deeper systematic transformation of the whole energy sector. Comprehensive regulatory, legal and financial frameworks will need to enable a decentralized and proactive organization of the energy sector with high shares of renewable energy.
Municipal solid waste (MSW) and other solid waste streams offer an excellent base for decentralized and localized power generation. They are widely available: in 2020, close to 70 billion tons of waste was generated around the world and different types of solid waste fractions made up some 20 billion tons. Only a few percent of this mass was recycled as raw materials or for energy making it the perfect fuel source for immediate deployment. Realistically, 50% of the solid waste could be utilized in power generation producing over 5,000 TWh annually, or 20% of the global electricity consumption.
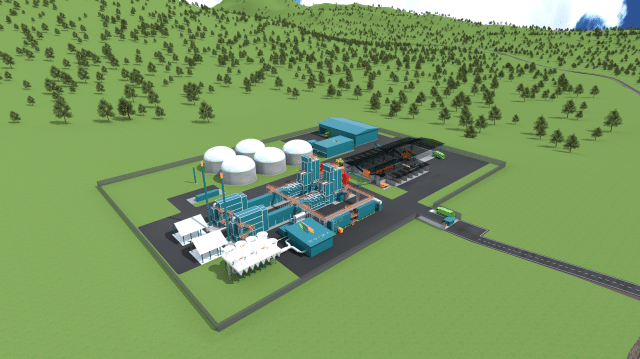
The WOIMA waste-to-value solutions support recycling and can utilize both newly collected and already landfilled waste in power generation. They have been designed to serve medium-sized cities and communities as a localized solution or capital and mega-cities as a decentralized waste management and power generation solution. Our WOIMA solutions have been developed with two key targets in mind; reducing the waste-induced challenges and simultaneously utilizing local fuel (waste) and employing local people to generate local wellbeing. It adheres to the strictest European emission directives and reduces the waste-related water, soil and air emissions to practically zero.
Read case study: Decentralized W2E power generation in Nairobi, Kenya
Free use case: Decentralized Waste-to-Energy solution
FIND OUT MORE ABOUT WOIMA WASTE-TO-VALUE SOLUTIONS
CHECK YOUR WASTE CHARACTERISTICS
CONTACT US
WOIMA Corporation is a Finnish supplier of best-in-class waste-to-value products, projects and services worldwide. We have developed solutions that enable us, and the customer, to transform and recycle virtually any waste stream into raw materials and energy. At WOIMA we combine Finnish engineering know-how in waste management with power generation design expertise. These solutions are used in Finland every day. They support the circular economy ideology and ensure that less than 1% of Finland’s waste ends up in landfills.
Our mission is to improve quality of life both locally and globally, as well as empower people to utilize waste as a commodity. Our decades of international project management experience ensure an on-time, in-budget and high-quality WOIMA solution delivery across the globe.