Finding the Right Solution in the Emerging Market
As the global demand for clean energy sources increases, so too does the need for effective carbon capture technologies. With the emergence of a variety of options, it can be difficult to determine which technology is best suited for a particular application. This article provides a comprehensive comparison of the different carbon capture technologies available on the market, allowing businesses to make informed decisions when selecting the right solution for their needs.
The world is facing a climate crisis, and the need for carbon capture technology is becoming increasingly pressing. Climate change is the result of human activities that release carbon dioxide (CO2) and other heat-trapping gases into the atmosphere, and carbon capture technology is essential for mitigating and reversing this trend. Carbon capture technology is a set of methods for trapping and storing CO2.
Carbon capture systems are generally broken down into two main categories: direct air capture (DAC) and post-combustion capture (PCC). DAC systems capture CO₂ from the atmosphere directly, while PCC systems capture CO₂ from the exhaust of combustion sources such as power plants, automobiles, and factories. The DAC and PCC technologies have both advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to consider the unique requirements of each application when evaluating the right carbon capture solution.
Direct air capture (DAC) technology utilizes large-scale, energy-intensive systems to capture CO₂ directly from the atmosphere. DAC systems generally rely on sorbent materials, such as amine-based liquids, to attract and store CO₂ from the air. The CO₂ is then stored in a secure form or utilized in chemical industry or synthetic fuel production. The primary benefit of DAC systems is their scalability; they are capable of capturing large amounts of CO₂ from the atmosphere. However, DAC systems also have several drawbacks. These systems require a substantial amount of energy to operate, and they can be expensive to install and maintain. Additionally, the sorbent materials used in DAC systems can be sensitive to temperature and humidity, making them susceptible to breakdown in certain climate conditions.
Post-combustion capture (PCC) technology captures CO₂ from the exhaust of combustion sources. PCC systems generally use amine-based liquids, scrubbing solvents, or adsorptive materials to capture the CO₂ from the exhaust gases. The captured CO₂ can then be stored or utilized similar to DAC products. The primary benefit of PCC systems is their cost-effectiveness; they are generally cheaper to install and operate than DAC systems. PCC systems also require less energy than DAC systems, making them more efficient and easier to maintain. Additionally, PCC systems are capable of capturing larger amounts of CO₂ than DAC systems, making them attractive for large-scale projects. However, PCC systems also have several drawbacks. These systems require frequent maintenance and can be limited in their scalability. Additionally, PCC systems are only capable of capturing CO₂ from combustion sources, meaning they cannot capture CO₂ from the atmosphere.
Amine-based liquids, scrubbing solvents such as HPC, and adsorptive materials all have their own unique pros and cons when it comes to their application in CO2 capture. Depending on the specific application, one of these three methods might be more suitable than the others.
Amine-based liquids are considered to be one of the most efficient and cost-effective methods of capturing CO2 in an industrial setting. The process of using amine-based liquids is relatively simple. The CO2 is absorbed into the liquid and then released when the liquid is heated. One of the main advantages of using amine-based liquids include their ability to capture large amounts of CO2 in a relatively short amount of time. Additionally, the process of heating and releasing the CO2 is relatively energy efficient. However, the main disadvantages of using amine-based liquids is the fact that they are often proprietary, i.e. typically costly, corrosive, and potentially hazardous to human health and the environment. In addition, the cost of purchasing and disposing of the chemicals used in this process can be expensive.
Scrubbing solvents such as HPC are another mainstream in the capture of CO2. HPC has the advantage of being able to capture CO2 in a much smaller volume than amine-based liquids. Additionally, HPC is not corrosive or hazardous. Other benefits include widely available low-cost solvent, hundreds of references across different industries and no solvent degradation during the process. However, the process of using HPC is more energy-intensive than the process of using amine-based liquids, making it potentially more costly.
Adsorptive materials are another type of material used in the capture of CO2. These materials have the advantage of being able to capture CO2 in a much smaller volume than either amine-based liquids or HPC. Additionally, adsorptive materials are not corrosive or hazardous. However, the process of using adsorptive materials is more energy-intensive than the other two methods, and it can be expensive to purchase and dispose of the materials used in this process.
Overall, each of the three methods of capturing CO2 has its own unique advantages and disadvantages. The method that is chosen for a particular application will depend on the specific needs of the process and the amount of energy and cost that is available. By carefully considering the pros and cons of each method, a facility can determine which method is best suited for its particular application.
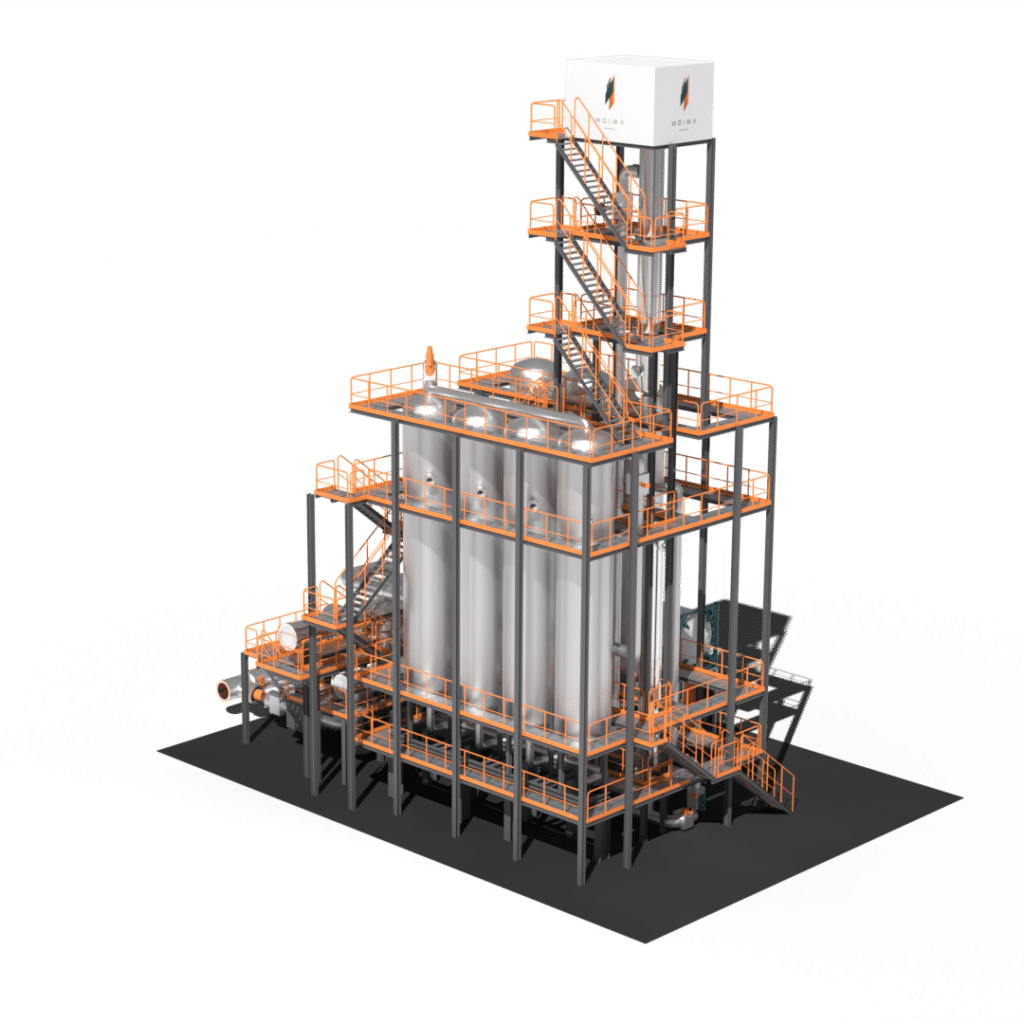
Our offering to the carbon capture market, the standardized, scalable, and modular ccWOIMA® carbon capture plant is an energy-efficient HPC-based process capturing 20,000 to 200,000 tpa. of CO2 out of the power plant’s flue gas stream. It combines seamlessly with our small-scale wasteWOIMA® waste-to-energy power plant providing carbon-neutral, or even carbon-negative, baseload power.
Read more about our waste-to-energy solutions below.
READ MORE ABOUT OUR WASTEWOIMA® CCUS SOLUTION
READ MORE ABOUT OUR WASTE-TO-ENERGY SOLUTIONS
Read more about us at www.woimacorporation.com
WOIMA Corporation is a Finnish supplier of best-in-class waste-to-value products, projects and services worldwide. We have developed solutions that enable us, and the customer, to transform and recycle virtually any waste stream into raw materials and energy. At WOIMA we combine Finnish engineering know-how in waste management with power generation design expertise. These solutions are used in Finland every day. They support the circular economy ideology and ensure that less than 1% of Finland’s waste ends up in landfills.
Our mission is to improve quality of life both locally and globally, as well as empower people to utilize waste as a commodity. Our decades of international project management experience ensure an on-time, in-budget and high-quality WOIMA solution delivery across the globe.